WordPress multisite is a type of WordPress installation that allows you to manage several sites from a single administration panel.
With multisite, it is possible to create any number of sites within a single WordPress instance.
Here we will describe in more detail how multisite mode works and when it is worth using it.
How WordPress multisite works
Each instance within WordPress multisite has access to the same set of themes and plugins and database, but has its own separate directory of files uploaded to the server (assets).
Shared code, separated data
Each instance within the network shares a code base: WP installation, plugins, themes/themes.
What is separate is the data: each site has its own set of selected database tables (for posts, taxonomies, comments, links and options). So each site has its posts and its media library (and a directory for uploads on the server).
Users are kept in one table, but a user registered on one site does not automatically have access to the panels of all other sites on the network. If user wants to access another site’s panel, he/she must be manually added/invited by that site’s administrator or by a super administrator.
WordPress multisite functionality can be added to a new or existing installation.
Subdomains or subdirectories
Subsequent websites within the multisite can be registered as subdomains, e.g. subdomain.example.com or subdirectories, e.g. example.com/subdirectory.
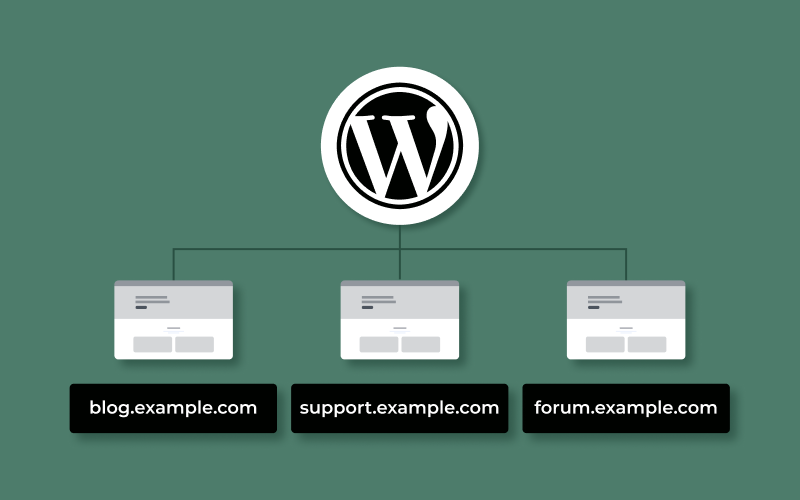
It is not possible to have some sites in subdomains and some in subdirectories at the same time. You choose this setting once when configuring/installing your network (you can change it later, but it’s not so easy anymore).
Note: some web hosts may not allow adding more domains/subdomains and then multisite installation would only be possible in subdirectories.
It is also possible to create a multisite site with its own domain in a multidomain network. In that case, the individual sites in the multisite network could have different domains:
example1.com example2.com, etc.
Super administrator role
As a result of multisite activation, WordPress gives the main administrator the role of Super Administrator, who can update the entire network, i.e. WP version and all plugins/themes, from one place. The Super Administrator has full access to all features across the multisite network.
The Super Administrator can also add more sites, install themes and plugins. He can also create new administrators or users and grant them appropriate permissions.
Each site can be disabled or enabled, archived or restored, and deleted. Each site also has its own set of basic settings (such as date format, default number of posts per page, default thumbnail dimensions, etc.).
When to use WordPress Multiste?
WordPress multisite is well suited for creating sets of websites with similar functionality and can be used for many types of projects.
“Similar functionality” means using a similar set of plugins and/or theme based on the main code (child theme).
WordPress Multisite can be used to create websites within a single company. It can be used to create blogs, and universities often use multisite to give employees the ability to create blogs within their network.
A good example of this is blogs.harvard.edu, for example.
All users with the email address “name@harvard.edu” can create their own blog within the blogs.harvard.edu subdomain.
Multisite works well when a company opens a new branch and needs a separate website.
WordPress Multisite is also very often used to create different language versions for a single site.
When not to use WordPress Multisite?
In some cases, you should avoid using multisite functionality.
You should not use multisite if you want to manage several separate websites, each with different functions and purposes. If a site has completely different functional needs than the other sites and adds a set of plugins or code to the network that is not used anywhere else, it should not be part of the network, but a separate installation.
All sites within Multisite use the same database, so if you want a separate, different database for any of the sites, WordPress Multisite will be a bad choice.
Advantages and disadvantages of WordPress Multisite
Advantages:
- ability to manage all sites from one CMS panel.
- plugins and themes are global making them more convenient to manage
- updates are done only once for all sites in the network
- easier backup – one copy for all sites
- convenience and savings – one hosting account for the whole network of sites
Disadvantages:
- not all plugins are compatible with multisite
- hacking attack or failure of one site from the network will affect all other sites in the same network
- heavy traffic on one site may slow down the others
- more powerful hosting is required for proper operation (you need to consider the requirements of all sites on the network)
Examples of WordPress multisite usage
- https://wordpress.com – (probably the biggest example)
- http://blogs.harvard.edu
- https://www.bbcamerica.com – BBC America








